The Jagannath Temple, located in the city of Puri in the eastern state of Odisha, India, stands as a monumental symbol of religious devotion, cultural heritage, and architectural grandeur. With a history that dates back centuries, this sacred site dedicated to Lord Jagannath, a form of the Hindu deity Vishnu, holds immense significance for millions of devotees and visitors alike. This article delves into the rich history, intricate architecture, religious practices, vibrant festivals, and the profound impact of the Jagannath Temple on Odisha’s culture and society.
1. History of Jagannath Temple
Origins and Founding
Legend has it that the Jagannath Temple in Puri, India, was founded in ancient times by King Indradyumna. The temple is dedicated to Lord Jagannath, a form of the Hindu god Vishnu.
Evolution and Expansion
Over the centuries, the temple has undergone several renovations and expansions. The current structure dates back to the 12th century when it was rebuilt by King Anantavarman Chodaganga Deva of the Eastern Ganga dynasty.
2. Architecture and Design
Temple Layout and Features
The Jagannath Temple complex covers a vast area and is known for its towering spire, intricate carvings, and sacred tanks. The main temple is surrounded by smaller shrines, halls, and gardens.
Sculptures and Artwork
The temple is adorned with exquisite sculptures depicting various deities, animals, and mythical creatures. The artwork inside the temple showcases a blend of Odishan and Dravidian architectural styles.
3. Significance and Religious Practices
Importance of Lord Jagannath
Lord Jagannath is believed to be a symbol of unity and equality, attracting devotees from all walks of life. The deity is worshipped not only in Puri but also in many other parts of India.
Pilgrimage and Devotional Practices
The temple is a major pilgrimage site, with millions of devotees visiting each year to seek blessings and participate in rituals. Devotees engage in various practices like offering prayers, performing rituals, and observing fasts.
4. Annual Festivals and Rituals
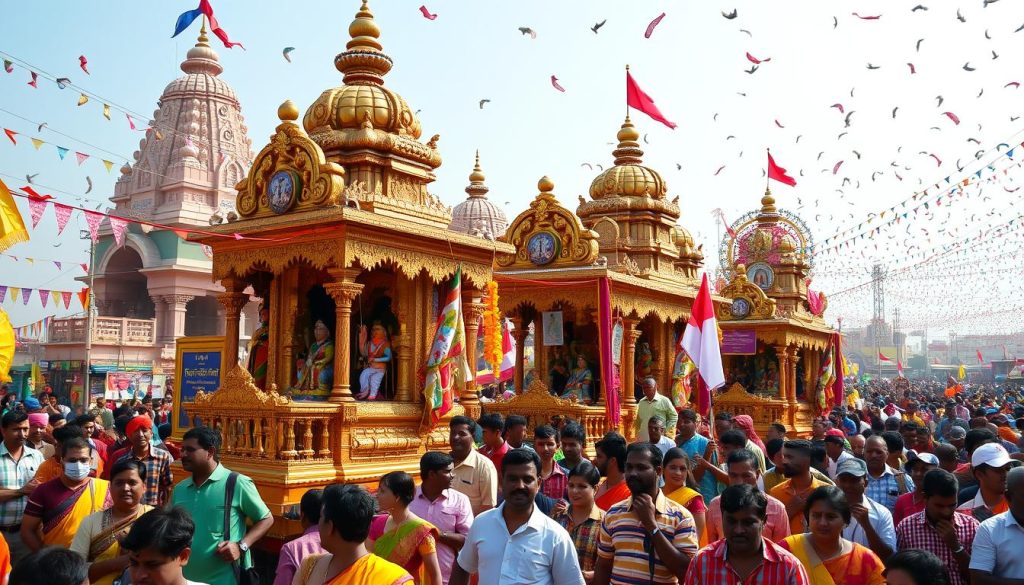
Rath Yatra – Chariot Festival
The Rath Yatra, or Chariot Festival, is a grand annual event where idols of Lord Jagannath, his siblings Balabhadra and Subhadra, are taken out in giant chariots for a procession. It is one of the most famous festivals in India.
Snana Yatra – Bathing Ritual
The Snana Yatra is a ritual where the deities are bathed with 108 pitchers of water infused with herbs and perfumes. This ceremonial bathing is considered highly auspicious and attracts a large gathering of devotees.
5. Role in Odisha Culture and Society
Socio-cultural Impact
The Jagannath Temple holds a significant place in Odisha’s culture and society, acting as a beacon of religious devotion and tradition. It serves as a unifying force, bringing people from all walks of life together to partake in rituals, festivals, and spiritual practices.
Economic Contributions and Tourism
Apart from its cultural importance, the Jagannath Temple also plays a crucial role in the economy of Odisha. The temple attracts a large number of pilgrims and tourists, contributing to the local economy through offerings, donations, and tourism-related activities. The temple complex supports a thriving ecosystem of businesses that cater to the needs of visitors, creating employment opportunities and boosting the region’s economy.In conclusion, the Jagannath Temple continues to stand as a beacon of spirituality and tradition, drawing pilgrims and tourists from far and wide to witness its magnificence and partake in its sacred rituals. With its blend of history, architecture, religious fervor, and cultural importance, the temple remains a vital cornerstone of Odisha’s identity and a cherished symbol of faith for generations to come.
- New Year Evening Superstitions
- Can I apply for PMAY if I already own a house
- How to Apply for Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana
- Similipal National Park
- Bhitarkanika national park odisha